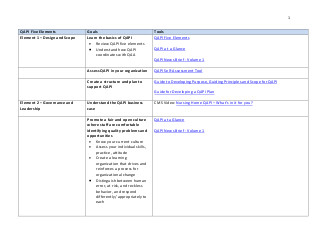
Five Elements of QAPI
Element 5: Systematic Analysis and Systemic Action
The facility uses a systematic approach to determine when in-depth analysis
is needed to fully understand the problem, its causes, and implications of
a change. The facility uses a thorough and highly organized/ structured
approach to determine whether and how identified problems may be caused or
exacerbated by the way care and services are organized or delivered.
Additionally, facilities will be expected to develop policies and
procedures and demonstrate proficiency in the use of Root Cause Analysis.
Systemic Actions look comprehensively across all involved systems to
prevent future events and promote sustained improvement. This element
includes a focus on continual learning and continuous improvement.
https://www.cms.gov/medicare/provider-enrollment-and-certification/qapi/downloads/qapiataglance.pdf


WHAT IS QAPI?
QAPI is the merger of two complementary approaches to quality management, Quality Assurance (QA) and Performance Improvement (PI). QA and PI combine to form QAPI, a comprehensive approach to ensuring high quality care. Both involve seeking and using information, but they differ in key ways:
- QA is a process of meeting quality standards and assuring that care reaches an acceptable level. Nursing homes typically set QA thresholds to comply with regulations. They may also create standards that go beyond regulations. QA is a reactive, retrospective effort to examine why a facility failed to meet certain standards. QA activities do improve quality, but efforts frequently end once the standard is met.
- PI (also called Quality Improvement - QI) is a proactive and continuous study of processes with the intent to prevent or decrease the likelihood of problems by identifying areas of opportunity and testing new approaches to fix underlying causes of persistent/systemic problems. PI in nursing homes aims to improve processes involved in health care delivery and resident quality of life. PI can make good quality even better.
ELEMENT 5 – Systematic Analysis and Systemic Action
Getting to the Root of the Problem (Systematic Analysis)Root cause analysis (RCA) provides a structure for evaluating events (e.g., adverse event, incident, near miss, unsafe condition, or complaint). The RCA process looks at events and incidents from a systems perspective. RCA avoids focusing on individual performance as a cause of errors or events, and instead focuses on the underlying breakdowns or gaps in the systems or processes in which individuals are working. The key question in RCA is “why?”. The goal of RCA is not to describe what happened, but to understand why things happened or are done a certain way. If the underlying root causes of performance can be identified, changes can be made to improve current performance and prevent future occurrences.
Steps of the RCA process include:
- Describing the details of the event so everyone can picture the steps that occurred and where decisions were made. This includes who, what, where, and when.
- Looking for root causes and their preceding factors as well as any contributing factors that added to the likelihood of the problem or event occurring. This may require owcharting processes to see where there are gaps or breakdowns. The most important thing to do in this step is to keep asking “why” or “why did the process fail” until you just can’t go any further. Failure to do this can lead to corrective actions that do not address true underlying causes and you may not decrease your risk of the problem or event recurring.
- Sorting identified gaps or breakdowns into categories such as:
- Human factors such as communication, training, distraction, or bias
- Rules, policies, or procedures. Was there a problem with current policies or procedures or are there no policies or procedures to address an issue?
- Environment/equipment
- Barriers – was this a breakdown in a barrier or defensive mechanism that was intended to prevent the problem?
- Clearly identifying the root cause(s) and contributing factor(s).
- Identifying corrective actions to address the root causes and put a plan in place to measure the impact of these interventions.
Focus on a specific problem. One of the challenges when you first start using RCA is defining the problem or the event in such a way that it is not too broad. For example, RCA on medication errors will quickly get too big. Instead, identify the various types of medication errors that are occurring and use the RCA process to better understand each type. By looking at several types of medication errors you will start to see common causes or contributing factors that can be addressed with a broader intervention.
Root Cause Analysis is an excellent tool for performance improvement because it helps identify the root causes and contributing factors that led to an event or that if changed can improve performance. However, identifying root causes is only the first step. Next you will need to implement changes or corrective actions at the system level. This will result in improvement or reduce the chance of the event recurring. Often this step is the weakest link in the process, as solutions often center on training/ education or asking clinicians to “be more careful.”
These common solutions do not impact the system, and are based on two assumptions: lack of knowledge contributed to the event, and if a person is educated or trained the mistake won’t happen again. Solutions that rely on vigilance or memory are equally problematic because they create expectations for staff to remember more or be more careful. This is not always realistic when staff are in stressful situations or when multi-tasking.
To be effective, interventions or corrective actions should target elimination of root causes, offer long term solutions to the problem, and be achievable, objective, and measurable.
The Department of Veterans Affairs National Center for Patient Safety’s Hierarchy of Actions classifies corrective actions as:
WEAK: Actions that depend on staff to remember their training or what is written in the policy. Weak actions enhance or enforce existing processes.
Examples of Weak Actions:
- Double checks
- Warnings/labels
- New policies/procedures/ memoranda
- Training/education
INTERMEDIATE: Actions that are somewhat dependent on staff remembering to do the right thing, but they provide tools to help staff to remember or to promote clear communication. Intermediate actions modify existing processes.
Examples of Weak Actions:
- Decrease workload
- Software enhancements/ modi cations
- Checklists/cognitive aids/ triggers/prompts
- Read back
- Enhanced documentation/ communication
STRONG: Actions that do not depend on staff to remember to do the right thing. The action may not totally eliminate the vulnerability but provides strong controls. Strong actions change or re-design the process. They help detect and warn so there is an opportunity to correct before the error reaches the patient. They may involve hard stops which won’t allow the process to continue unless something is corrected or gives the chance to intervene to prevent significant harm.
Examples of Strong Actions:
- Physical changes: grab bars, nonslip strips on tubs/showers
- Forcing functions: design of gas lines so that only oxygen can be connected to oxygen lines;
- Electronic medical records – cannot continue charting unless all fields filled in; need to step on brake before car can be put into reverse
- Simplifying: unit dose

|
QAPI Five Elements |
Goals |
Tools |
|---|---|---|
|
Element 5 – Systematic Analysis and Systemic Action |
Understand and focus on organizational processes and systems
|
Guidance for Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) Guidance for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Flowcharting Five Whys Fishbone Diagram |